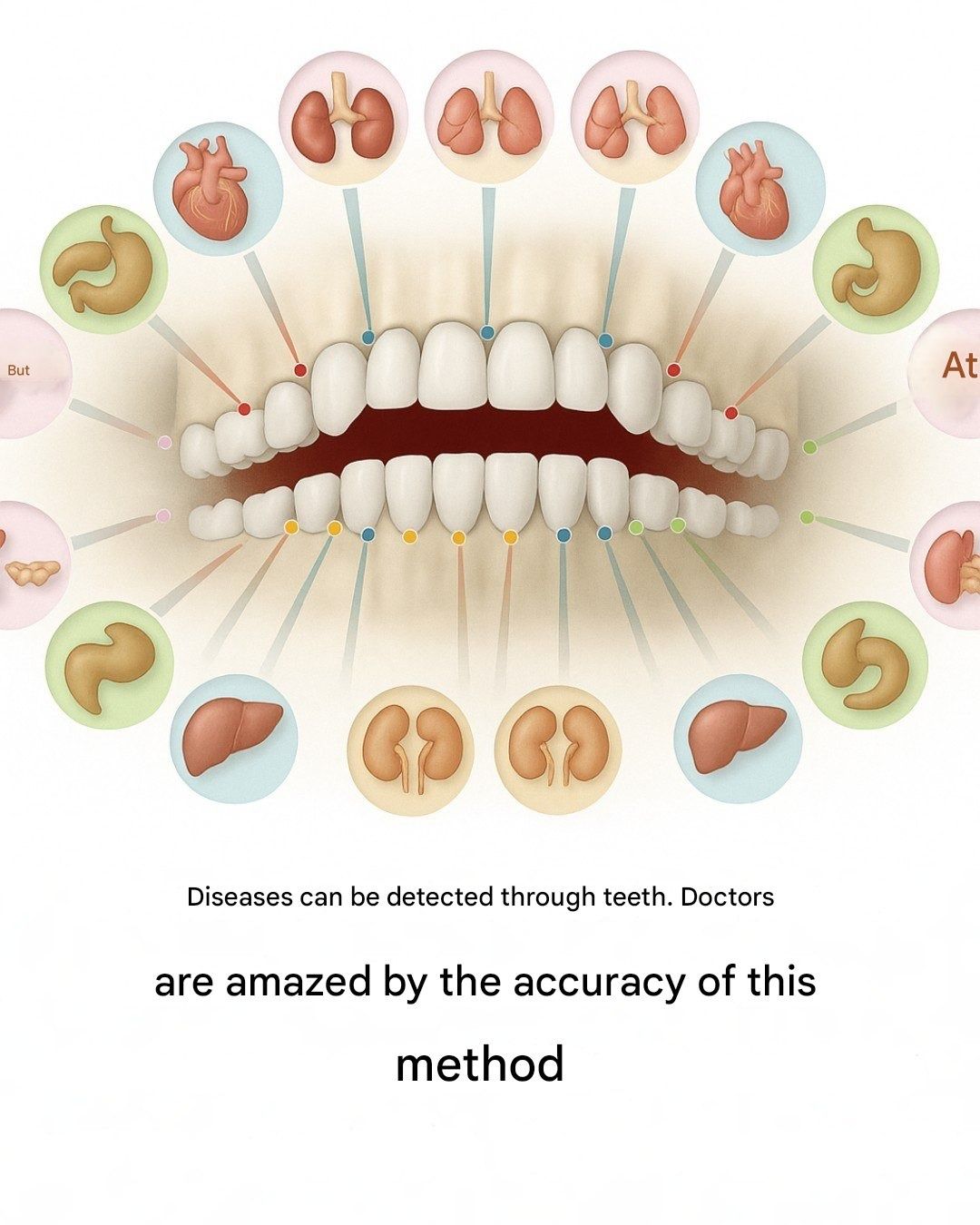
The sensation of a toothache is almost universally recognized as a sharp, localized distress—a signal that usually prompts an immediate appointment with a dentist to address a cavity, a fractured crown, or an abscess. However, within the realms of holistic health and ancient medical traditions, the mouth is viewed not as an isolated mechanical system, but as a sophisticated dashboard for the entire human body. This perspective suggests that our teeth are much more than tools for mastication; they are sentinels that guard and reflect the health of our internal organs. According to the “dental meridian” theory, each individual tooth is energetically connected to a specific organ or system through the body’s meridian pathways, meaning that a persistent ache in a structurally sound tooth might actually be a siren song from an imbalanced kidney, a struggling liver, or a stressed heart.
To understand this interconnectedness, one must view the body as a complex circuit board where energy channels, or meridians, facilitate communication between seemingly unrelated parts. When a blockage or ailment occurs in an internal organ, the distress signal can manifest as sensitivity or pain in the corresponding tooth. This dental meridian map provides a framework for interpreting oral discomfort as a diagnostic tool for broader systemic issues. By categorizing the teeth into specific groups, we can begin to decode the language of the body’s warning systems and potentially identify future health problems before they become acute.
The journey through the dental map begins with the incisors, the sharp front teeth located in both the upper and lower jaws. These prominent teeth are believed to be the primary indicators for the kidneys and the urinary system. If a patient experiences recurring sensitivity or dull aches in the incisors that a dentist cannot explain through traditional x-rays, it may be a sign of a deeper imbalance within the urinary tract. Proponents of this theory suggest that such dental pain could be a precursor to chronic pyelonephritis, a bladder infection, or even issues related to the middle ear, such as otitis media. Because the kidneys are essential for filtering toxins and maintaining fluid balance, discomfort in the front teeth serves as a vital prompt to evaluate one’s renal health and hydration levels.
SEE CONTINUES ON THE NEXT PAGE